Staff Dr. Martin Lenz

Contact Information
Endenicher Allee 60
53115 Bonn
Teaching
Winter semester 2025/26
Summer semester 2025
See teaching activities of the whole group.
Research Projects
Current
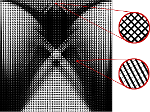
Numerical optimization of shape microstructures
Project C06, DFG SFB 1060.
Completed
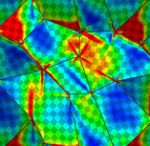
Mathematical modeling and simulation of microstructured magnetic-shape-memory materials
Project A6, DFG priority program 1239.
The macroscopic behavior of magnetic shape-memory (MSM) materials is largely determined by the formation of fine-scale structures, both in the elastic and in the magnetic degrees of freedom. Most practically used samples exhibit additional inhomogeneities on the mesoscale, such as for example the grain structure in polycrystals. The interaction of the two types of microstructure is up to now only poorly understood. Focusing on two occurrences of high current experimental relevance we intend to investigate the role of microstructure for the macroscopic material behavior, and to furnish criteria to improve material production. Building upon the static continuum model developed in the first phase, which permits to resolve the magnetic and elastic structure at scales much smaller than the domain size, we plan:
1) to consider the experimentally relevant case of grains larger than the domain size, where the magnetoelastic behavior of a grain is determined by averaging over the domains;
2) to study dynamics and in particular hysteresis by formulating an evolutionary problem which resolves the motion of individual domain boundaries; and
3) to study the dynamics for grains larger than the domain size, with an averaged version of the evolution model. For each issue we shall address the development of a model, the numerical implementation of the obtained models, and the application to the study of MSM-polymer composites and MSM polycrystals.
Publications
-
-
-
-
-
Homogenization in magnetic-shape-memory polymer composites.
S. Conti, M. Lenz, M. Pawelczyk, and M. Rumpf.
In V. Schulz and D. Seck, editors, Shape Optimization, Homogenization and Optimal Control : DFG-AIMS workshop held at the AIMS Center Senegal, March 13-16, 2017, pages 1–17.
Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2018.
BibTeX
DOI
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Homogenization in magnetic-shape-memory polymer composites. S. Conti, M. Lenz, M. Pawelczyk, and M. Rumpf. In V. Schulz and D. Seck, editors, Shape Optimization, Homogenization and Optimal Control : DFG-AIMS workshop held at the AIMS Center Senegal, March 13-16, 2017, pages 1–17. Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2018. BibTeX DOI